MANGANESE SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE GENE POLYMORPHISM IS NOT ASSOCIATED WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION IN SLOVENE TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS
Abstract
Aim: to investigate an association between the V16A MnSOD gene polymorphism and myocardial infarction (MI) in Slovene type 2 diabetic patients.
Patients and methods: in this case-control cross-sectional study a relationship between the alanine/valine single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) at amino acid sequence 16 of manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD) gene and myocardial infarction (MI) in Slovene type 2 diabetic patients was evaluated.
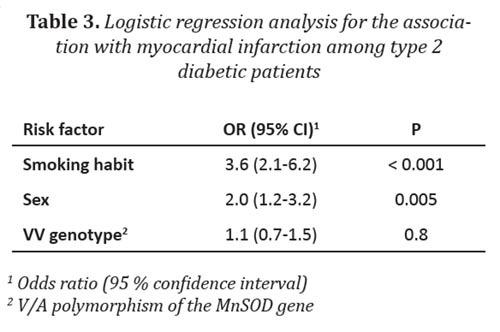
Results: the V16A polymorphism of the Mn-SOD gene was analysed in 449 subjects with type 2 diabetes lasting more than 10 years: 159 with MI (diabetics with MI) and 290 diabetics with no history of CAD. The VV genotype of the V16A Mn-SOD SNP was not associated with MI in Slovene patients with type 2 diabetes (OR = 0.9; 95 % CI = 0.6-1.5; P = 0.7).
Conclusion: the V16A Mn-SOD SNP might not be used as a genetic marker for MI in Slovene type 2 diabetic patients.
Keywords
DOI: 10.5457/ams.v38i2.96
