EFFECT OF URINE SAMPLE COLLECTION METHOD ON CONTAMINATION RATE OF URINE CULTURE
Abstract
Introduction: Urine sample for biochemical analysis must fulfill certain criterions. The sample collection must be done by following established standards so that the results of analysis are reliable. In children of various age, especially during serious disease, adequate consideration must be devoted to this procedure.
Aims: To evaluate contamination rate of the urine sample according to the methods of obtaining samples and collecting specimens in seriously sick children of various age during their intensive treatment.
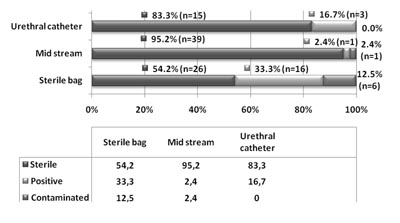
Methods: Urine culture findings in children treated in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) of Children’s Hospital in Tuzla in period from January 2007 to the end of December 2007 were included in retrospective analysis according to the method of collecting (bag collection, urethral catheterization, clean catch). In all of the three groups the percentage of positive findings and percentage of contaminated specimens as well as sex related distribution was analyzed. The urine sample was obtained from urethral catheter only in patients with indication for urethral catheterization. Kruskal-Wallis test and regression model were used in statistical analysis. Results: A total of 662 children were treated in ICU during the observed period. The urine sample for routine biochemical tests was obtained from all patients. In 107 patients (16.2 %) urine culture examination was indicated. In 48 (44.9%) patients urine sample was obtained by bag collection, in 41 (38.3%) by clean catch, and 18 (16.8%) by urethral catheterization. In 7 patients or 6.5% urine was contaminated. The majority of contaminated specimens were collected by bag (12.5%). In 20 (18.7%) patients urine culture was positive with significant number of etiologic agents and 80 (74.8%) specimens were negative. Difference in results in three monitored groups was statistically significant which was confirmed by Kruskal-Wallis test and stepwise regression model.
Conclusion: Obtaining urine sample by bag collection brings the highest risk for contamination.
Keywords
DOI: 10.5457/ams.v38i1.29
